SoCTAssist Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project created by the SE-EDU initiative.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
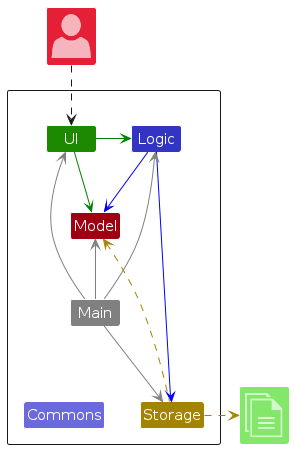
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
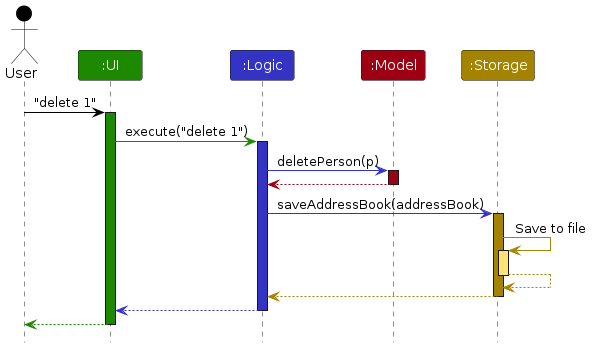
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
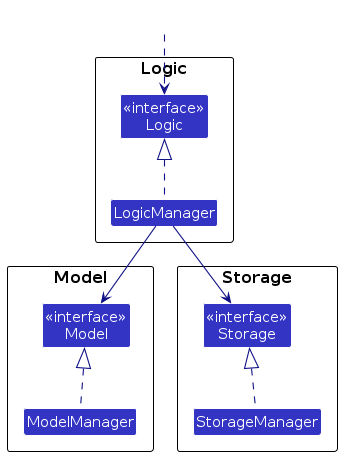
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
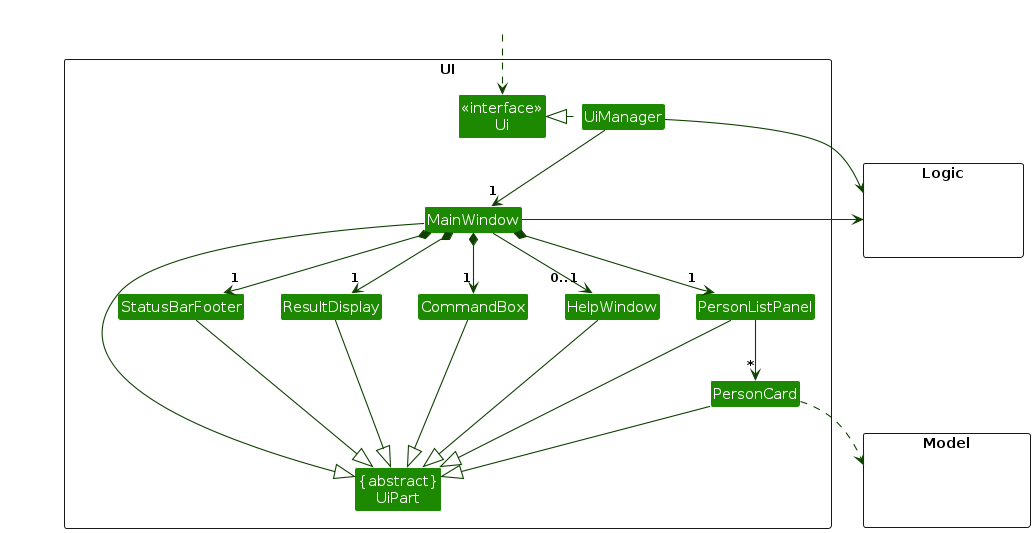
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
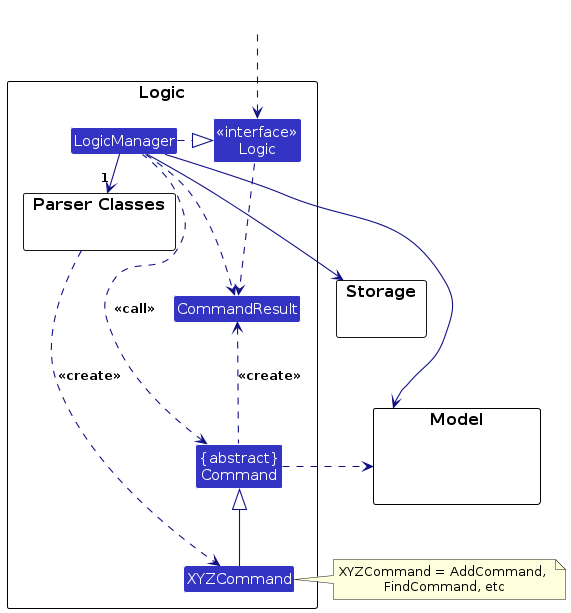
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
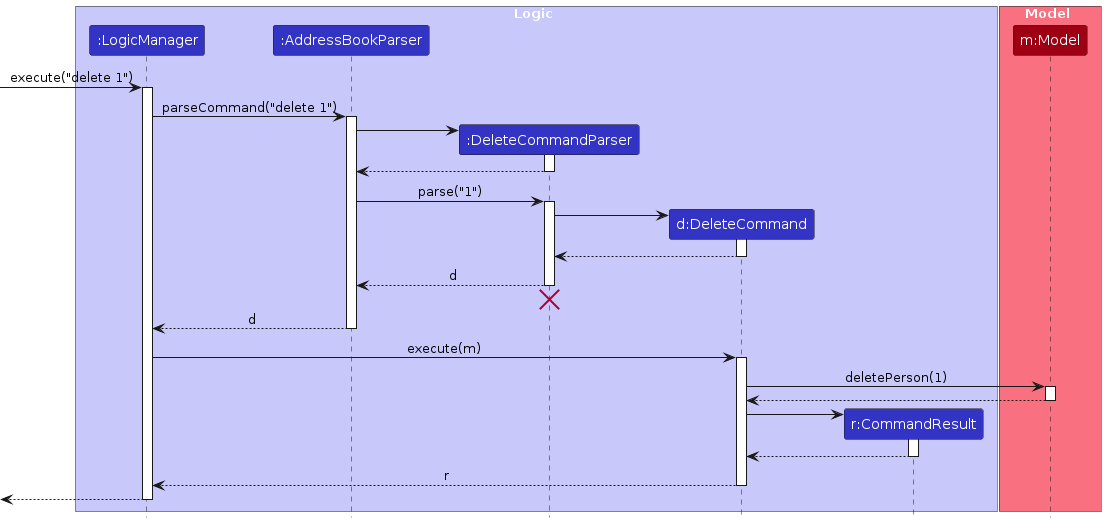
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anAddressBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a person).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user
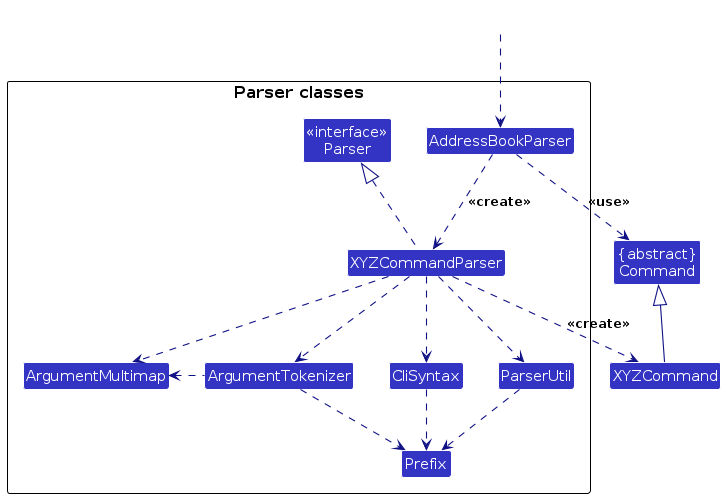
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
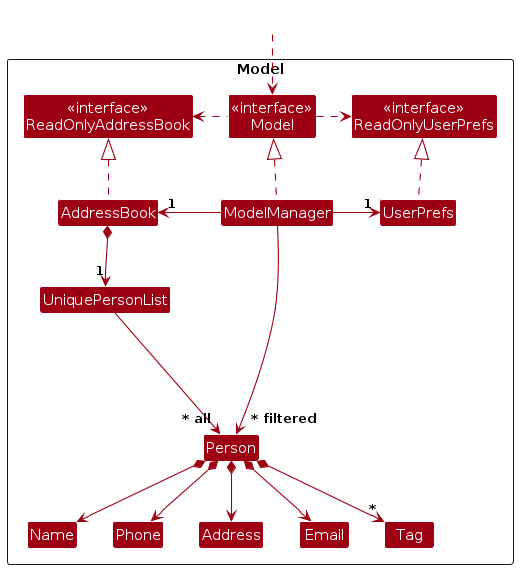
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Storage component
API : Storage.java
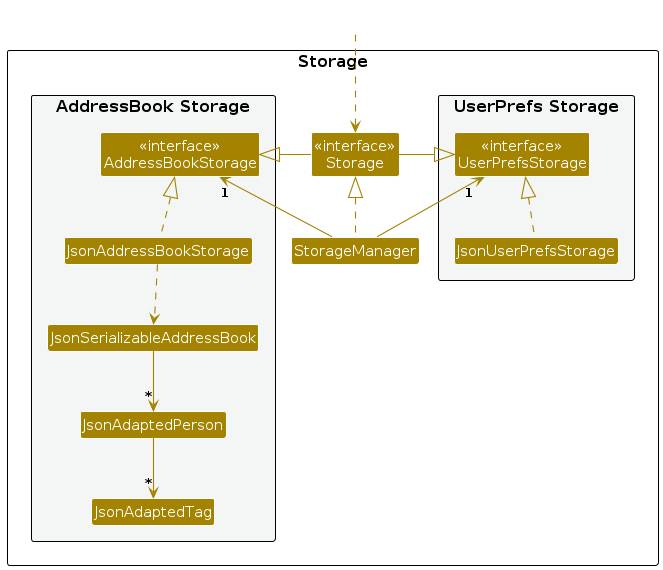
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Add Homework Feature
The add homework feature allows users to assign a homework task to either a specific student or all students. Each homework is identified by an assignment ID.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for adding homework:
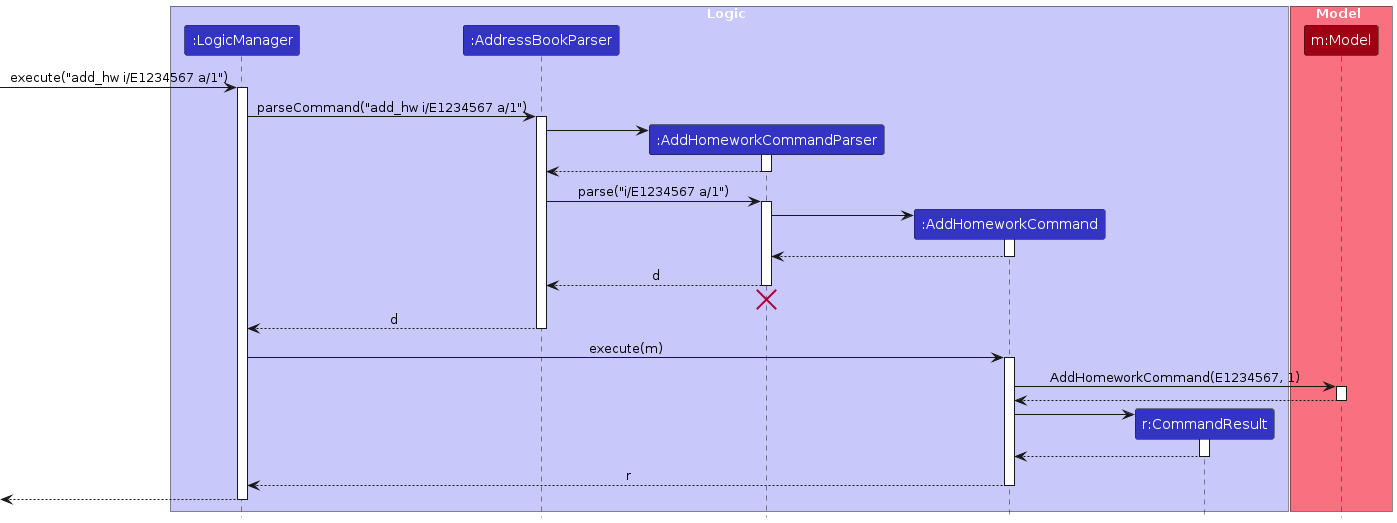
Note: The lifeline for AddHomeworkCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.
How the add_hw command works:
- When the user enters an
add_hwcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates anAddHomeworkCommandParserto parse the command arguments.AddHomeworkCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID (or the keywordall) and the assignment ID.- An
AddHomeworkCommandobject is created and executed. AddHomeworkCommandchecks if the homework assignment already exists for the specified student(s).- If no duplicates are found, the homework is added to the target student(s)’ homework tracker(s).
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
Delete Homework Feature
The delete homework feature allows users to remove an existing homework assignment from a specific student or from all students.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for deleting homework:
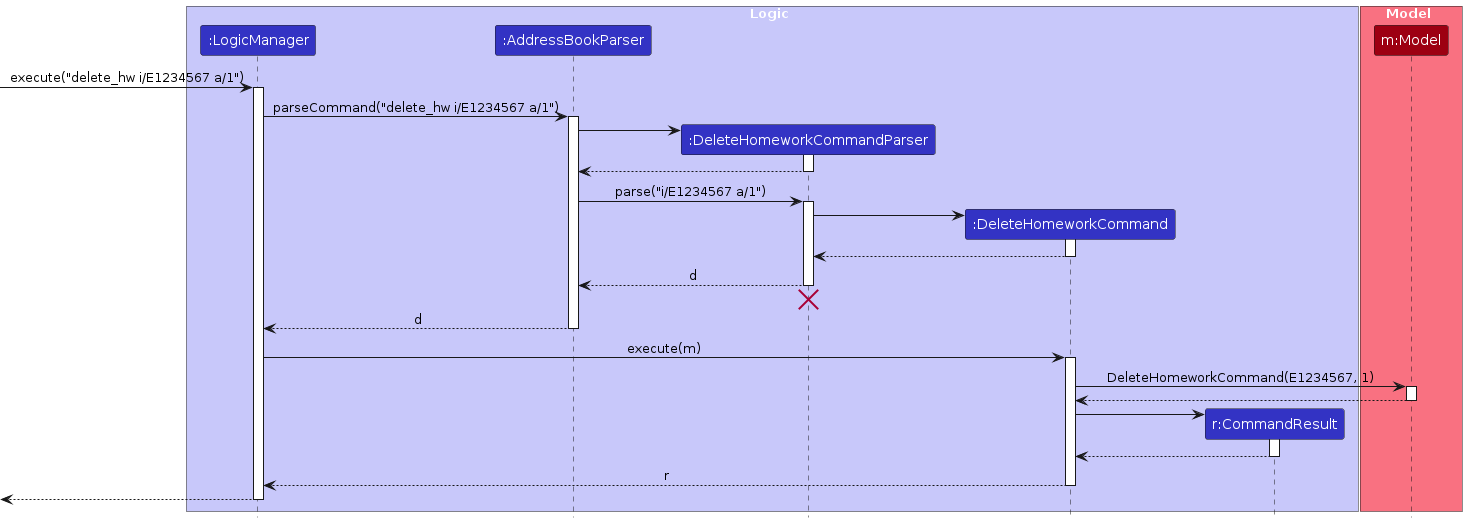
Note: The lifeline for DeleteHomeworkCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.
How the delete_hw command works:
- When the user enters a
delete_hwcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aDeleteHomeworkCommandParserto parse the command arguments.DeleteHomeworkCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID (or the keywordall) and the assignment ID.- A
DeleteHomeworkCommandobject is created and executed. DeleteHomeworkCommandverifies that the homework exists for the specified student(s).- If found, the homework is removed from the respective homework tracker(s).
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
Mark Homework Feature
The mark homework feature allows users to update the status (e.g., complete, incomplete, late) of a homework assignment for a specific student.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for marking homework:
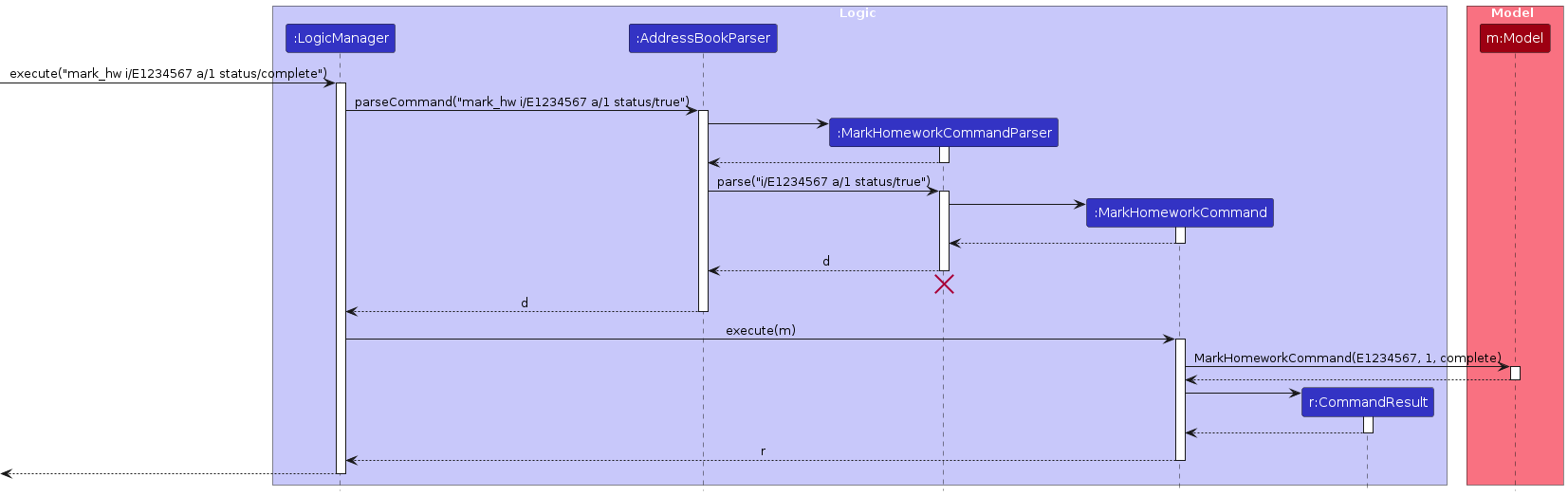
Note: The lifeline for MarkHomeworkCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.
How the mark_hw command works:
- When the user enters a
mark_hwcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aMarkHomeworkCommandParserto parse the command arguments.MarkHomeworkCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID, assignment ID, and status.- A
MarkHomeworkCommandobject is created and executed. MarkHomeworkCommandchecks whether the specified homework exists for the student.- If found, the homework’s status is updated to the new value.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
Mark Attendance Feature
The mark attendance feature allows users to mark the attendance status (e.g., present, absent, excused) of a single student in a particular week.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for marking attendance:
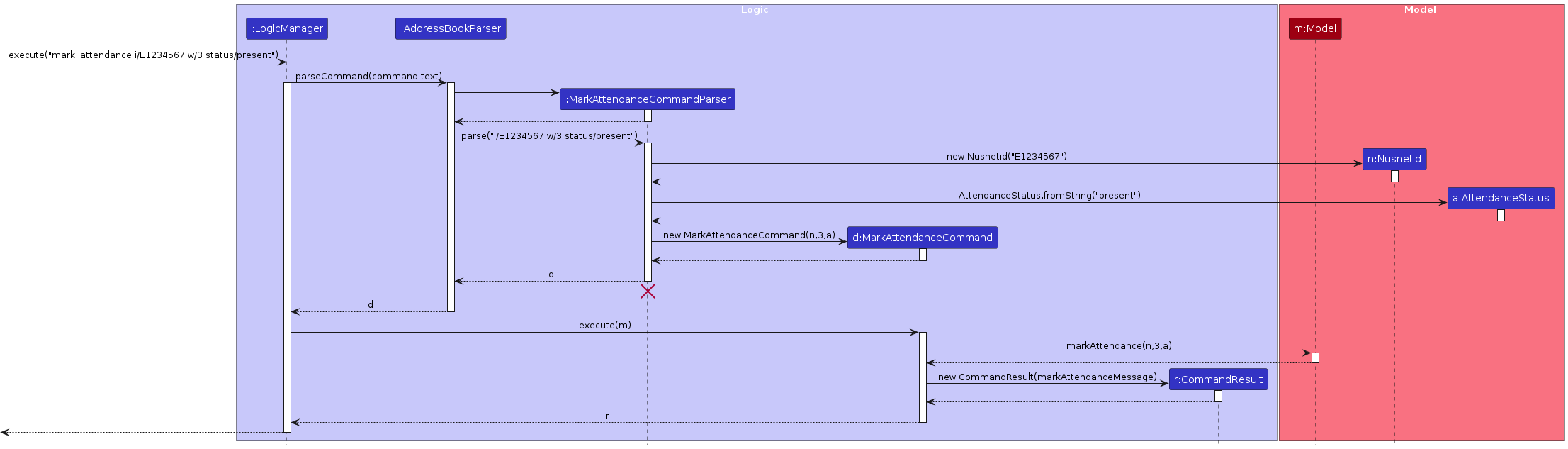
Note: The lifeline for MarkAttendanceCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.Due to limited space in the diagram, some input parameters(command text, markAttendanceMessage) are not explicitly shown in the diagram.
How the mark_attendance command works:
- When the user enters a
mark_attendancecommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aMarkAttendanceCommandParserto parse the command arguments.MarkAttendanceCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID, week number, and attendance status.- A
MarkAttendanceCommandobject is created and executed. MarkAttendanceCommandchecks whether the specified student exists.- If exists, the attendance status of the student in the specified week is updated to the status.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
Mark All Attendance Feature
The mark all attendance feature allows users to mark the attendance status (e.g., present, absent, excused) of a group of students in a particular week.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for marking attendance:
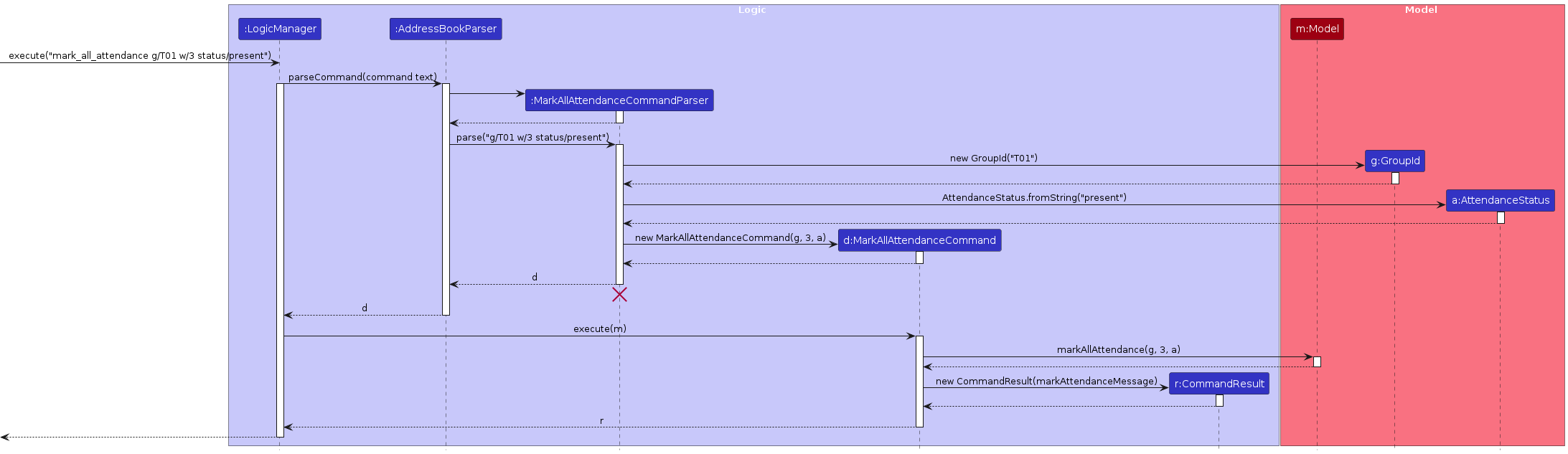
Note: The lifeline for MarkAllAttendanceCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram. Due to limited space in the diagram, some input parameters(command text, markAttendanceMessage) are not explicitly shown in the diagram.
How the mark_all_attendance command works:
- When the user enters a
mark_all_attendancecommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aMarkAllAttendanceCommandParserto parse the command arguments.MarkAllAttendanceCommandParservalidates and parses the GroupId, week number, and attendance status.- A
MarkAllAttendanceCommandobject is created and executed. MarkAllAttendanceCommandchecks whether the specified group exists.- If exists, the attendance status of students of the group in the specified week is updated to the status.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
Add Consultation Feature
The add consultation feature allows users to add consultation slots for students.
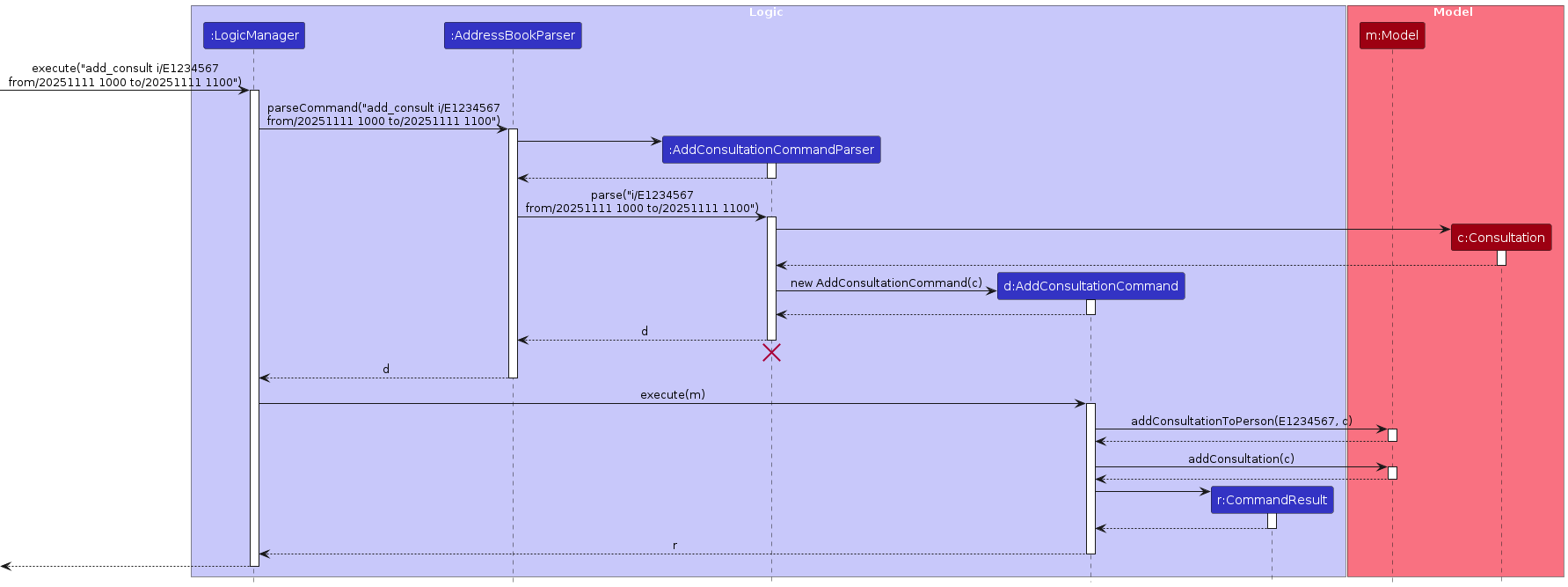
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for adding a consultation:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Model component for adding a consultation:
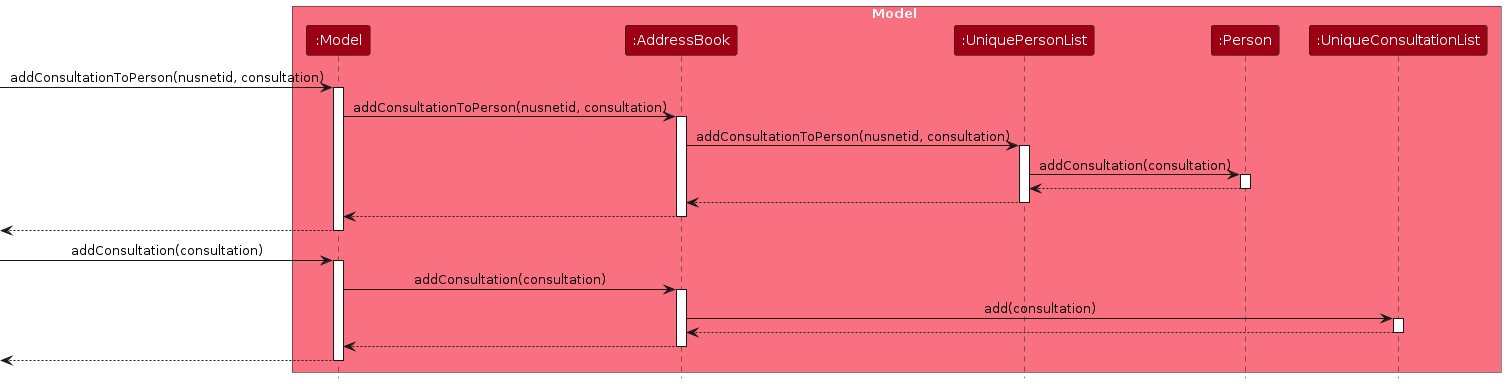
How the add_consult command works:
- When the user enters an
add_consultcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates anAddConsultationCommandParserto parse the command arguments.AddConsultationCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID, start time and end time.- An
AddConsultationCommandobject is created and executed. - During execution,
AddConsultationCommandchecks if the student exists in the model, if the consultation overlaps with other existing consultations in the model, and if the student already has a consultation. - If all checks pass, the consultation is added to the student and the model is updated.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
- A success message is returned to the user.
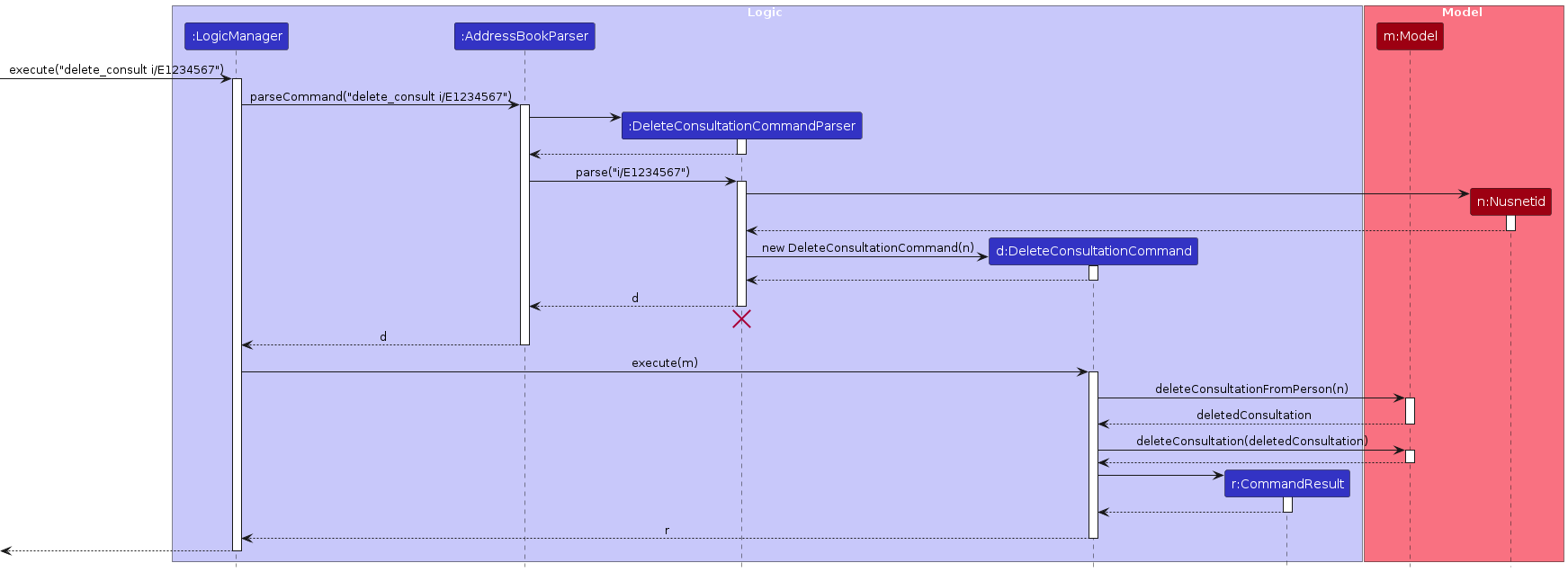
Delete Consultation Feature
The delete consultation feature allows users to delete existing consultations from students.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for deleting a consultation:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Model component for deleting a consultation:
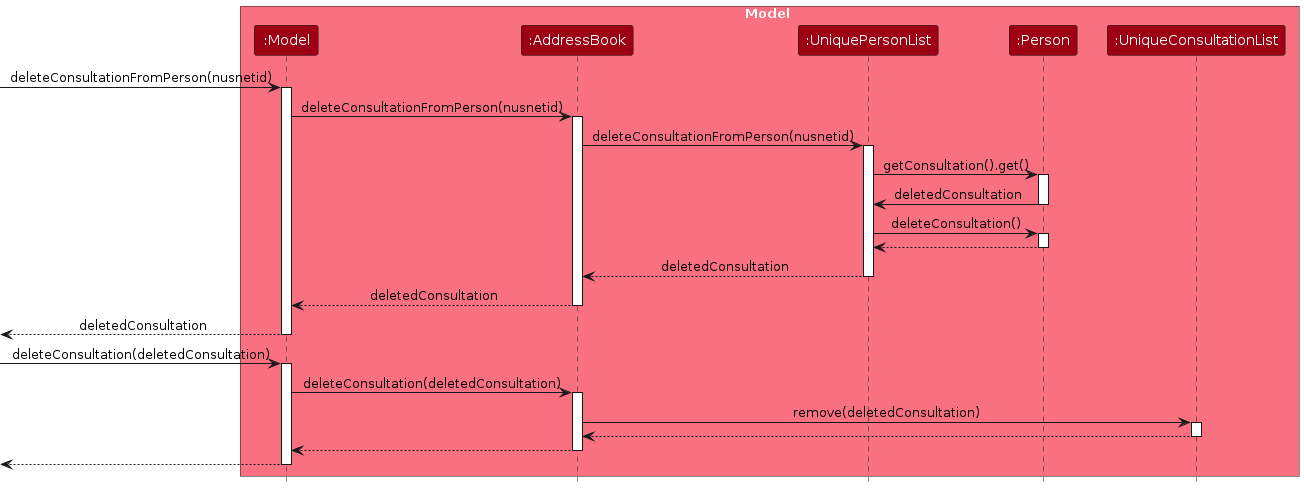
How the delete_consult command works:
- When the user enters a
delete_consultcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aDeleteConsultationCommandParserto parse the command arguments.DeleteConsultationCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID.- A
DeleteConsultationCommandobject is created and executed. - During execution,
DeleteConsultationCommandchecks if the student exists in the model and if the student has an existing consultation. - If both checks pass, the consultation is removed from the student and the model is updated.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
- A success message is returned to the user.
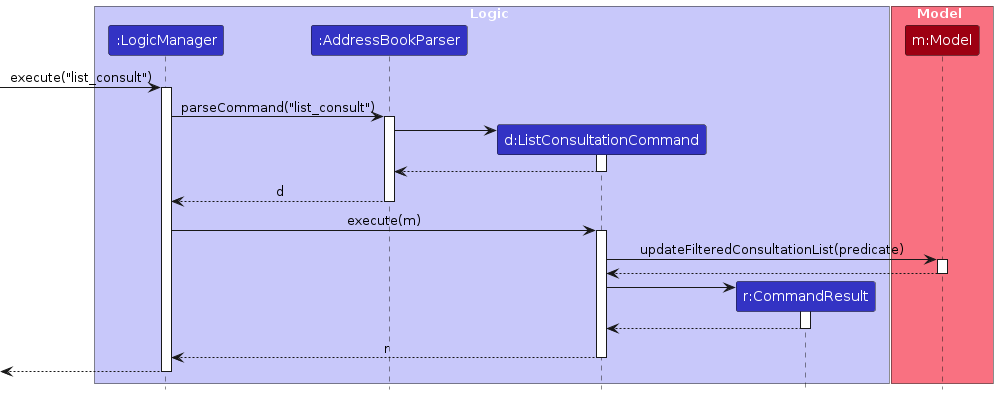
List Consultation Feature
The list consultation feature allows users to view all scheduled consultations.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for listing consultations:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Model component for listing consultations:
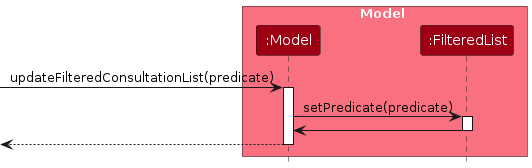
How the list_consult command works:
- When the user enters a
list_consultcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aListConsultationCommandobject.- The
ListConsultationCommandobject is executed. - During execution,
ListConsultationCommandupdates the filtered consultation list in the model. - A success message is returned to the user.
Create Group Feature
The create group feature allows users to create a new group by specifying a unique group ID.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic and Model component for creating a group:
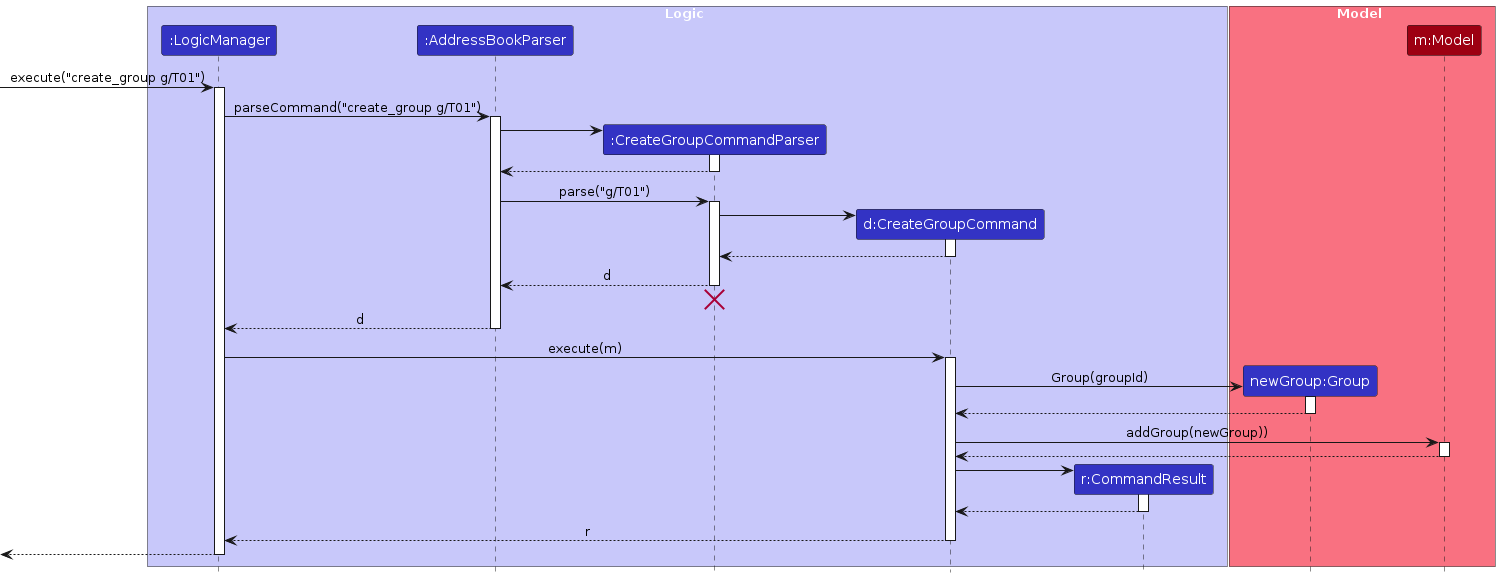
Note: The lifeline for CreateGroupCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.
How the create_group command works:
- When the user enters a
create_groupcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aCreateGroupCommandParserto parse the command arguments.CreateGroupCommandParservalidates and parses the group ID.- A
CreateGroupCommandobject is created and executed. CreateGroupCommandchecks if the group ID already exists.- If no duplicates are found, a new group is created with the specified group ID.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
Add Student to Group Feature
The add student to group feature allows users to assign a student to an existing group by specifying the student's NUSNET ID and the group ID.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic and Model component for adding a student to a group:
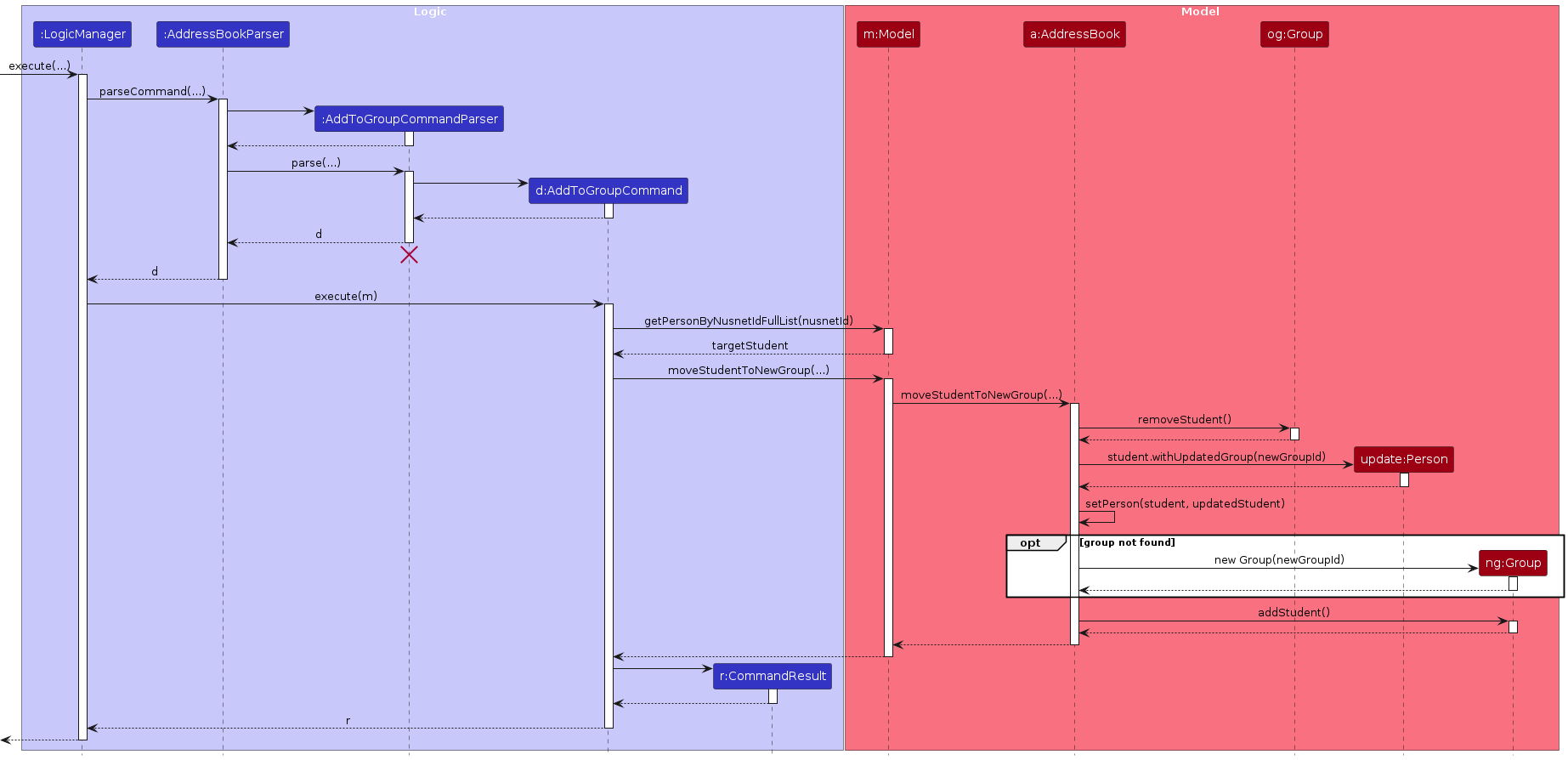
Note: The lifeline for AddToGroupCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.
How the add_to_group command works:
- When the user enters an
add_to_groupcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates anAddToGroupCommandParserto parse the command arguments.AddToGroupCommandParservalidates and parses the NUSNET ID and group ID.- An
AddToGroupCommandobject is created and executed. AddToGroupCommandchecks if the specified student exist.- If the student exists,
AddToGroupCommandchecks if the specified group already exist. - Create an updated student object with the new group ID.
- If the group exists, the student is added to the specified group.
- Else, the group is created and the student is added to the newly created group.
- The updated address book is saved to storage.
- If the student does not exist, an error message is shown to the user.
Find Student by Group Feature
The find student by group feature allows users to search for students belonging to a specific group by specifying the group ID.
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic and Model component for finding students by group:
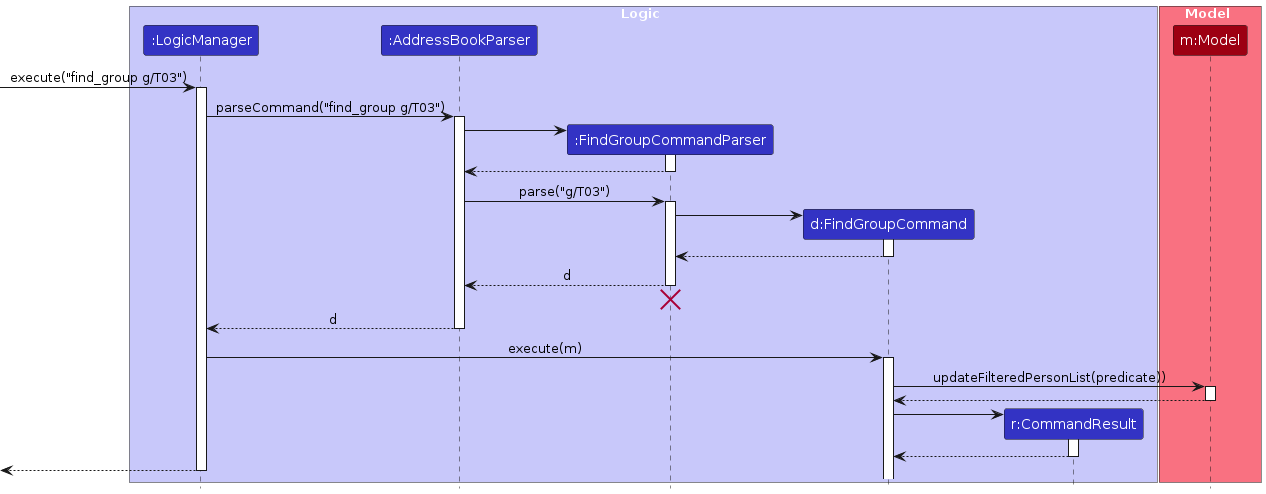
Note: The lifeline for FindGroupCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X), but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of the diagram.
How the find_group command works:
- When the user enters a
find_groupcommand,LogicManagerpasses it toAddressBookParser. AddressBookParsercreates aFindGroupCommandParserto parse the command arguments.FindGroupCommandParservalidates and parses the group ID.- A
FindGroupCommandobject is created and executed. - If the group ID is valid, and the group exist in the address book,
FindGroupCommandretrieves the list of students belonging to the specified group from theModel. - The filtered student list in the
Modelis updated to only include students from the specified group. - The updated filtered student list is displayed to the user in the UI.
- If the group ID is invalid, an error message is shown to the user.
- If the group does not exist, inform the user that no such group exists.
- No change to the address book is made.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
Teaching assistants (TAs) for Computer Science courses at the National University of Singapore (NUS) who
- needs to manage a group of students (e.g., a tutorial class), with the following responsibilities:
- mark attendance
- schedule consultations with students
- grade homework/assignments
- track students' progress
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: a one-stop solution for TAs to manage their students more easily than a typical mouse/GUI driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | TA | add a new student | |
* * * | TA | delete a student | remove entries I no longer need or added by mistake |
* * * | TA | mark students' attendance | record all students' tutorial attendance |
* * * | TA | track each individual student's homework completeness | view their learning progress and identify students who are falling behind |
* * | new user | have a step-by-step usage instruction guide | learn how to use the app |
* * | course coordinator | view all TAs' availability | assign TAs to their preferred tutorial group |
* * | head TA | create subgroups within the course | assign students and TAs to their respective tutorial groups |
* * | head TA | key in students' scores | update students' scores after every exam |
* * | head TA | view overall course feedback from students | gather data to perform course analysis |
* * | TA | search for a specific student | view his/her contact details and progress |
* * | TA | create subgroups within the tutorial group | assign students to their project groups |
* * | TA | add consultation slots | schedule consultations with students |
* * | TA | check students' scores | track students' performance |
* * | TA | view students' feedback | gain insights on my teaching style and method |
* * | TA | update my availability | update my consultation schedule |
* | TA | copy contact information onto my clipboard | save time from manually copying students' contact details |
* | TA | export student list as PDF | print it out for marking attendance |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the SocTAssist and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC01 - Add a student
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to add a student by specifying required fields: full name, NUSNET ID, email, Telegram handle and optional fields: phone number, group ID.
SoCTAssist validates all fields.
SoCTAssist adds the student into the directory.
SoCTAssist shows the updated student list in the UI table.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. One or more required fields are missing.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error.
Use case ends.
2b. Email format is invalid.
2b1. SoCTAssist shows error.
Use case ends.
2c. Group ID format is invalid.
2c1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
2d. A student with the same nusnetid already exists.
- 2d1. SoCTAssist shows error.
Use case: UC02 - Edit a student
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to edit a student by specifying the index and updated fields.
SoCTAssist validates that the student exists.
SoCTAssist updates the student's details.
SoCTAssist shows confirmation message with updated student details.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Student index does not exist.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error:
The person index provided is invalid.Use case ends.
2b. Any updated field is invalid.
2b1. SoCTAssist shows corresponding validation error. (UC01 Extensions 2b, 2c).
Use case ends.
2c. Try to update group id.
2c1. SoCTAssist shows error and states the correct format.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC03 - Delete a student
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to list students.
SoCTAssist shows a list of students.
User requests to delete a specific student in the list.
SoCTAssist deletes the student.
SoCTAssist UI updated. Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The list is empty.
1a1. SoCTAssist shows error.
Use case ends.
3a. Student index does not exist.
- 3a1. SoCTAssist shows error.
Use case ends.
3b. Student index is invalid (not a number or is not positive).
3b1. SoCTAssist shows error.
Use case ends.
Use Case: UC04 - Create Homework
Actor: TA
MSS
User enters a command to create a new homework numbered 1 to 3 for a student using their NUSNET ID.
SoCTAssist locates the student homework record.
SoCTAssist validates the assignment ID.
SoCTAssist creates the new assignment with an initial status of
incomplete.SoCTAssist displays a success message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Student with the given NUSNET ID does not exist
2a1. SoCTAssist displays an error message.
Use case ends.
3a. Homework ID already exists for this student
3a1. SoCTAssist displays an error message.
Use case ends.
3b. Homework ID is invalid (not between 1–13)
3b1. SoCTAssist displays an error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC05 - Mark Homework completion
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to mark a homework status for a student using their NUSNET ID.
SoCTAssist locates the student homework record.
SoCTAssist verifies the homework ID.
SoCTAssist updates the homework status (complete / incomplete / late).
SoCTAssist shows a confirmation message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
2a. The student with the given NUSNET ID does not exist.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error message:
Student not found.Use case ends.
3a. The given assignment ID is invalid (not between 1-13).
3a1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
4a. The given status is invalid (not one of complete / incomplete / late).
4a1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
4b. The student already has a status recorded for this assignment.
4b1. SoCTAssist updates the record with the new status (last write wins).
Use case resumes at step 5.
Use case: UC06 - Delete a homework
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to delete a homework for a student using their NUSNET ID.
SoCTAssist locates the student homework record.
SoCTAssist verifies the homework ID.
SoCTAssist removes the corresponding homework record from the student’s tracker.
SoCTAssist shows a confirmation message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
2a. The student with the given NUSNET ID does not exist.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
3a. The given assignment ID is invalid.
3a1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
4a. The specified homework does not exist for the student.
4a1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC07 - Add a consultation
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to add a consultation by specifying student's NUSNET ID, start date & time, and end date & time.
SoCTAssist validates the NUSNET ID, dates, and times.
SoCTAssist creates the consultation booking for the student.
SoCTAssist shows success message with consultation details and displays list of consultations to user.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Student NUSNET ID does not exist in the directory.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
2b. End time is not after start time.
2b1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
2c. The new consultation overlaps with an existing one.
2c1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
2d. A consultation with identical date and time already exists.
2d1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
2d. Student already has an existing consultation.
2d1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
4a. The consultation exceeds 3 hours in duration.
4a1. SoCTAssist displays a reminder message.
Use case ends.
4b. The consultation is over or ongoing.
4b1. SoCTAssist displays a reminder message.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC08 - Delete a consultation
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to delete a consultation by specifying student's NUSNET ID.
SoCTAssist validates the NUSNET ID.
SoCTAssist locates the consultation record that matches the provided details.
SoCTAssist deletes the consultation from the system.
SoCTAssist shows success message confirming the deletion and displays list of consultations to user.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. NUSNET ID does not exist in the directory.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
3a. Student with specified NUSNET ID does not have a consultation.
3a1. SoCTAssist shows an error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC09 - Mark attendance
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to mark attendance for a student by specifying student NUSNET ID, week, and attendance status.
SoCTAssist validates that the student exists and the week and status are valid.
SoCTAssist records the attendance for the student.
SoCTAssist shows a confirmation message with details.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. Student NUSNET ID does not exist.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error:
Student not found.Use case ends.
2b. Attendance status is invalid (not Present or Absent or Excused).
2b1. SoCTAssist shows error:
Please enter present/absent/excused only.Use case ends.
Use case: Mark all attendance
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to mark attendance for a group of student by specifying GroupId, week, and attendance status.
SoCTAssist validates that the group exists and the week and status are valid.
SoCTAssist records the attendance for the student.
SoCTAssist shows a confirmation message with details.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. GroupId does not exist.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error:
Group not found.Use case ends.
2b. Attendance status is invalid (not Present or Absent or Excused).
2b1. SoCTAssist shows error:
Please enter present/absent/excused only.Use case ends.
2c. Week is invalid (input is not between 2 and 13 or is not an integer.").
2c1. SoCTAssist shows error:
Invalid Week. Week should be between 2 and 13 and be a positive integer..Use case ends.
2d. Group does not have students.
2d1. SoCTAssist shows error:
No students in the group..Use case ends.
Use case: UC10 - Create student groups
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to create a new group with a specified GroupId.
SoCTAssist validates the GroupId.
SoCTAssist creates the group.
SoCTAssist shows confirmation message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The GroupId is missing.
- 2a1. SoCTAssist shows error message, saying GroupId is missing.
Use case ends.
2b. The GroupId is invalid.
2c1. SoCTAssist shows error message and indicates the valid format for GroupId.
Use case ends.
2c. The GroupId is a duplicate.
2b1. SoCTAssist shows error message, saying GroupId already exists
Use case ends.
Use case: UC11 - Add student to a group
Actor: TA
MSS
User requests to add a student to an existing group using the student’s NUSNET ID and GroupId.
SoCTAssist verifies the student exists.
SoCTAssist checks whether the group id is the same as the student's existing group.
SoCTAssist checks whether the group exists.
SoCTAssist adds the student to the specified group.
SoCTAssist shows confirmation message.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The student with the NUSNET ID does not exist.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error message.
Use case ends.
3a. The group id is the same as the student's existing group.
3a1. SoCTAssist shows error message, saying student already in that group.
Use case ends.
4a. The group does not exist.
4a1. SoCTAssist creates the group.
Use case resumes at step 5.
Use case: UC12 - Find students by group
Actor: TA
Guarantees:
- If the GroupId is valid and exists, at least one student is found.
MSS
User requests to find students by specifying a GroupId.
SoCTAssist verifies the GroupId is valid.
SoCTAssist checks whether the group exists.
SoCTAssist retrieves the list of students in the specified group.
SoCTAssist displays the list of students in the UI.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The GroupId is invalid.
2a1. SoCTAssist shows error message and indicates the valid format for Group Id.
Use case ends.
3a. The group does not exist.
3a1. SoCTAssist informs the user that no such group exists.
Use case ends.
Non-Functional Requirements
1. Data Requirements
NFR-D1: Data Size
- Maximum 500 students
- Maximum 20 tutorial groups
- Support 12 weeks of attendance data (weeks 2-13)
- Support maximum 13 homework
- Maximum 1 consultation slot for each student
NFR-D2: Data Volatility
High Volatility Data (changes very frequently):
- Attendance records: updated every tutorial session (weekly)
- Homework completion status: updated as TAs mark assignments throughout the week
- Consultation slot bookings: students book and cancel constantly, especially before assessments
Medium Volatility Data (changes occasionally):
- Student contact information: might change once or twice per semester
- Group assignments: adjusted a few times during the semester
Low Volatility Data (rarely changes):
- Student directory (names, NUSNET IDs): mostly stable after add/drop period
- Tutorial group assignments: fixed after first few weeks
NFR-D3: Data Persistence
- All student data must persist between application sessions.
- Attendance, homework, and consultation records must be permanent until explicitly deleted.
- System must auto-save after every successful command.
2. Environment/Technical Requirements
NFR-E1: Operating System Compatibility
- Must run on Windows, Linux, and OS-X platforms.
- Must work on both 32-bit and 64-bit environments.
- No OS-dependent libraries or OS-specific features allowed.
- Cross-platform compatibility without any modifications to codebase.
NFR-E2: Software Dependencies
- Requires Java 17 only (no other Java version required or installed).
- Must work without internet connection (offline-first design).
- No external database server required.
- Third-party libraries must be:
- Free and open-source with permissive licenses
- Packaged within the JAR file (no separate installation required)
- Not require user account creation on third-party services
- Approved by teaching team prior to use
NFR-E3: Hardware Requirements(To be finalized later)
- The application must operate efficiently on standard consumer-grade hardware without requiring specialized equipment.
- Must run on both desktop and laptop computers without additional hardware dependencies.
3. Performance Requirements
NFR-P1: Response Time
- Basic commands must complete within 2 seconds.
- Find operations must return results within 2 second.
NFR-P2: Startup Time
- Application must launch within 5 seconds on standard hardware.
4. Scalability Requirements
NFR-S1: User Scalability
- Supports TAs managing multiple tutorial groups.
NFR-S2: Data Scalability
- Performance must not degrade noticeably up to 100 students.
5. Usability Requirements
NFR-U1: Learnability
- First-time TA users must be able to add a student and mark attendance within 10 minutes using the onboarding guide.
- The onboarding guide must be completable in under 5 minutes.
- Help command must provide examples for all commands.
NFR-U2: Efficiency
- Experienced users should be able to mark attendance for 30 students in under 2 minutes.
- Common tasks should require fewer than 3 commands.
- All primary functions must be accessible via keyboard commands without requiring mouse.
NFR-U3: Error Handling
- Error messages must be specific and actionable.
- System must provide confirmation prompts for destructive operations.
- No technical jargon in error messages - use plain language
NFR-U4: Consistency
- Command syntax must be consistent across all features using the same prefix style (i/, n/, e/, t/, status/, w/, a/).
- All command names follow verb-noun format:
add_student,mark_attendance,delete.
NFR-U5: Visual Design
- Minimum font size: 12pt for readability
- UI must be usable on minimum resolution 1280x720.
- Clear visual separation between tabs (Students, Attendance, Homework, Groups)
6.Constraints
NFR-C1: Constraint-Single-User
- The product should be for a single user i.e., (not a multi-user product).
- Not allowed: Application running in a shared computer and different people using it at different times.
- Not allowed: The data file created by one user being accessed by another user during regular operations (e.g., through a shared file storage mechanism).
NFR-C2: NoDBMS
- Do not use a DBMS to store data.
Glossary
Homework terms
- complete: The student has submitted the homework on time.
- incompleted: The student has not submitted the homework yet. When the user creates the homework, it is marked as incomplete by default.
- late: The student has submitted the homework, but has passed the deadline of the homework.
Attendance terms
- present: The student is present for the tutorial on that week.
- excused: The student did not come for the tutorial, but has a valid reason (e.g., on MC, has competition)
- absent: The student did not come for the tutorial, and does not have a valid reason.
Consultation terms
Ongoing: A consultation is ongoing if it has a start time before the current time and a end time after the current time.
(E.g. if the current time is
20251010 1700, a consultation from20251010 1600to20251010 1800is ongoing.)Over: A consultation is over if its end time is before the current time.
(E.g. if the current time is
20251010 1700, a consultation from20251010 1400to20251010 1600is over.)Overlap: A consultation overlaps with another consultation if its start time is before the other consultation's end time and its end time is after the other consultation's start time.
(E.g. a consultation from
20251010 1400to20251010 1600overlaps with a consultation from20251010 1559to20251010 1759but does not overlap with a consultation from20251010 1600to20251010 1800.)
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
This section provides step-by-step, comprehensive instructions for performing manual testing of the application. These steps ensure that testers can validate the app’s functionality, usability, and reliability without the need for automated test tools.
Note: These instructions serve as a foundation for manual testing. Testers are strongly encouraged to perform exploratory testing beyond the described cases to uncover edge cases and unexpected behaviors.
1. Launch and Shutdown Tests
1.1 Initial Launch
Download and Setup:
- Obtain the latest
soctassist.jarfile of the application. - Copy the
soctassist.jarfile into a new, empty folder to avoid interference from previous data files.
- Obtain the latest
Launch Application:
- Double-click the
soctassist.jarfile to start the application. - Open a terminal or command prompt in the folder containing the .jar file.
- Run the following command:
java -jar soctassist.jar
- Expected Result:
- The main GUI should appear with a set of sample data (e.g., sample students).
- The window size and position may initially not be optimized.
- The app should not crash or freeze upon startup.
- Double-click the
1.2 Saving Window Preferences
Change and Save Window State:
- Resize and reposition the main application window.
- Close the application normally.
Re-launch Application:
Deleting a person
- Open the
soctassist.jarfile again. - Expected Result:
- The window should reopen at the same size and position as before.
- All layout and visual preferences should persist across restarts.
2. Data Management Tests
2.1 Deleting a person (Functional Test)
Preparation:
- Use the
listcommand to ensure that multiple persons are visible in the list.
- Use the
Valid Deletion Command:
- Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message.
Command:
delete 1Expected Result:
- The first person in the list is deleted.
- The status bar updates with the details of the deleted student.
- The total count of persons decreases by one.
- Test case:
Invalid Deletion Commands:
Try the following commands:
delete 0delete(no index)delete x(where x is greater than the list size)
Expected Result:
- Appropriate error messages displayed.
- No data is deleted.
3. Saving and Loading Data
3.1 Data Persistence Check
Add a few entries (new students).
Close and reopen the application.
Expected Result:
- All newly added data should reappear, confirming that data was correctly saved to disk.
4. User Interface and Command Behavior
4.1 Command Validation
Test all supported commands (e.g.,
add,edit,list,help) with correct and incorrect parameters.Expected Result:
- Correct commands execute successfully.
- Incorrect ones show meaningful error messages (no technical jargon).
4.2 Keyboard Accessibility
- Verify that all major commands can be executed via keyboard only.
- Expected Result: No mouse interaction should be required for primary operations.
4.3 Error Message Clarity
Trigger various input errors intentionally.
Expected Result:
- Messages should explain what went wrong and how to fix it.
- Messages should use simple, clear language.
5. Exploratory Testing Suggestions
- Try adding invalid characters.
- Test compatibility on different operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux).
Add homework
Add homework to a single student
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
add_hw i/E1234567 a/1 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Added assignment 1 for <STUDENT_NAME> (default incomplete). - The student’s homework tracker now includes homework 1, marked as incomplete by default.
- The command box is cleared and ready for the next input.
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
Add homework to all students
- Setup: Ensure multiple students are present in the system.
- Execute the command:
add_hw i/all a/2 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Added assignment 2 for all students (default incomplete). - All students’ homework trackers now contain homework 2.
Add homework (Student not found)
- Setup: Ensure the student with the NUSNET ID E0000000 is not present in the system.
- Execute the command:
add_hw i/E0000000 a/3 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Student with NUSNET ID E0000000 does not exist. - No homework is added.
Add homework (Missing parameters)
- Execute the command:
add_hw a/1 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Invalid command format! <With the rest of helping information> - No homework is added.
- Execute the command:
Add homework (Invalid homework ID: out of range)
- Execute the command:
add_hw i/E1234567 a/100 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Homework id must be between 1 and 13. - No homework is added.
- Execute the command:
Add homework (Duplicate prefixes)
- Setup: Make sure that the person with NUSNET ID E1234567 already has homework 1
- Execute the command:
add_hw i/E1234567 a/1 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Homework 1 already exists for <STUDNET_NAME>. - No homework is added.
Summary of Expected Results
| Test Case | Command | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | add_hw i/E1234567 a/1 | ✅ Homework 1 added to student E1234567 |
| 2 | add_hw i/all a/2 | ✅ Homework 2 added to all students |
| 3 | add_hw i/E0000000 a/3 | ❌ Student not found |
| 4 | add_hw a/4 | ❌ Missing NUSNET ID |
| 5 | add_hw i/E1234567 a/14 | ❌ Homework ID out of range |
| 6 | add_hw i/E1234567 i/E7654321 a/1 | ❌ Duplicate prefixes |
Delete homework
Delete homework from a single student
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567, and that the student already has homework 1 assigned. - Execute the command:
delete_hw i/E1234567 a/1 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Deleted homework 1 for <STUDENT_NAME>. - Homework 1 is removed from the student’s homework tracker.
- The command box is cleared and ready for the next input.
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
Delete homework from all students
- Setup: Ensure multiple students are present in the system, each with homework 2 assigned.
- Execute the command:
delete_hw i/all a/2 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Deleted homework 2 for all students. - Homework 2 is removed from every student’s homework tracker.
Delete homework (Student not found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
E0000000in the system. - Execute the command:
delete_hw i/E0000000 a/1 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Invalid NUSNET ID format. - No homework is deleted.
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
Delete homework (Missing parameters)
- Execute the command:
delete_hw a/1 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Invalid command format! <With the rest of helping information> - No homework is deleted.
- Execute the command:
Delete homework (Invalid homework ID: out of range)
- Execute the command:
delete_hw i/E1234567 a/100 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Homework id must be between 1 and 13. - No homework is deleted.
- Execute the command:
Delete homework (Homework not found)
- Setup: Ensure that the student with NUSNET ID
E1234567does not have homework 3 assigned. - Execute the command:
delete_hw i/E1234567 a/3 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Homework 3 not found for Alex Yeoh. - No homework is deleted.
- Setup: Ensure that the student with NUSNET ID
Delete homework (Duplicate prefixes)
- Execute the command:
delete_hw i/E1234567 i/E7654321 a/1 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Invalid command format! <With the rest of helping information> - No homework is deleted.
- Execute the command:
Summary of Expected Results
| Test Case | Command | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | delete_hw i/E1234567 a/1 | ✅ Homework 1 deleted from student E1234567 |
| 2 | delete_hw i/all a/2 | ✅ Homework 2 deleted from all students |
| 3 | delete_hw i/E0000000 a/1 | ❌ Student not found |
| 4 | delete_hw a/1 | ❌ Missing NUSNET ID |
| 5 | delete_hw i/E1234567 a/100 | ❌ Homework ID out of range |
| 6 | delete_hw i/E1234567 a/3 | ❌ Homework does not exist |
| 7 | delete_hw i/E1234567 i/E7654321 a/1 | ❌ Duplicate prefixes |
Mark homework
Mark homework as completed for a single student
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567, and that the student has homework 1 assigned. - Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 status/complete - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Assignment 1 for <STUDENT_NAME> marked complete.
- Homework **1** is now marked as **completed** in the student’s homework tracker. - The command box is cleared and ready for the next input.- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
Mark homework as incomplete for a single student
- Setup: Ensure homework 1 for student
E1234567is currently marked as completed. - Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 status/incomplete - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Assignment 1 for <STUDENT_NAME> marked incomplete. - Homework 1 is now marked as incomplete in the student’s homework tracker.
- Setup: Ensure homework 1 for student
Mark homework as late for a single student
- Setup: Ensure homework 2 is assigned to student
E1234567. - Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 a/2 status/late - Expected:
- Success message is displayed:
Assignment 1 for <STUDENT_NAME> marked late. - Homework 2 is now marked as late in the student’s homework tracker.
- Setup: Ensure homework 2 is assigned to student
Mark homework (Student not found)
- Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E0000000 a/1 status/complete - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Student not found - No homework is updated.
- Execute the command:
Mark homework (Homework not assigned)
- Setup: Ensure that student
E1234567does not have homework 3 assigned. - Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 a/3 status/complete - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Homework 3 does not exist for <STUDENT_NAME>. Add it first using 'add_hw'. - No homework is updated.
- Setup: Ensure that student
Mark homework (Invalid status)
- Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 status/done - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Status must be one of: complete, incomplete, late. - No homework is updated.
- Execute the command:
Mark homework (Missing parameters)
- Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Invalid command format! <With the rest of helping information> - No homework is updated.
- Execute the command:
Mark homework (Duplicate prefixes)
- Execute the command:
mark_hw i/E1234567 i/E7654321 a/1 status/complete - Expected:
- Error message is displayed:
Multiple values specified for the following single-valued field(s): i/ - No homework is updated.
- Execute the command:
Summary of Expected Results
| Test Case | Command | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 status/completed | ✅ Homework 1 marked completed |
| 2 | mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 status/incomplete | ✅ Homework 1 marked incomplete |
| 3 | mark_hw i/E1234567 a/2 status/late | ✅ Homework 2 marked late |
| 4 | mark_hw i/E0000000 a/1 status/completed | ❌ Invalid NUSNET ID |
| 5 | mark_hw i/E1234567 a/3 status/completed | ❌ Homework does not exist |
| 6 | mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 status/done | ❌ Invalid status |
| 7 | mark_hw i/E1234567 a/1 | ❌ Missing status parameter |
| 8 | mark_hw i/E1234567 i/E7654321 a/1 status/completed | ❌ Duplicate prefixes |
Mark Attendance
Mark attendance for a single student
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
mark_attendance i/E1234567 w/2 status/present - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is at least one student in the system with NUSNET ID
Mark attendance (Student not found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
E0000000in the system. - Execute the command:
mark_attendance i/E0000000 w/2 status/present - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
Mark attendance (Invalid week)
- Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
mark_attendance i/E1234567 w/20 status/present - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Mark attendance (Invalid status)
- Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
mark_attendance i/E1234567 w/2 status/late - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Mark All Attendance
Mark attendance for all students in one group
- Setup: Ensure group T01 with students present in the system.
- Execute the command:
mark_all_attendance g/T01 w/2 status/absent - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
Mark all attendance (Group not found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is no group with GroupID T02 in the system.
- Execute the command:
mark_all_attendance g/T02 w/2 status/present - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
Mark all attendance (Invalid week)
- Setup: Ensure group T01 with students present in the system.
- Execute the command:
mark_all_attendance g/T01 w/20 status/present - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
Mark all attendance (Invalid status)
- Setup: Ensure group T01 with students present in the system.
- Execute the command:
mark_all_attendance g/T01 w/2 status/late - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
Mark all attendance (Group has no students)
- Setup: Ensure group T03 exists but has no students in the system.
- Execute the command:
mark_all_attendance g/T03 w/2 status/present - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
Add Consultation
Add a consultation for a student
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567that has no consultation. - Execute the command:
add_consult i/E1234567 from/20251010 1400 to/20251010 1500 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
- List of consultations is updated to include the new consultation.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Add a consultation (Student not found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
E0000000in the system. - Execute the command:
add_consult i/E0000000 from/20251010 1400 to/20251010 1500 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
Add a consultation (End time before start time)
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234568. - Execute the command:
add_consult i/E1234568 from/20251010 1500 to/20251010 1400 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Add a consultation (Overlapping consultation)
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with a consultation from
20251010 1400to20251010 1500. Ensure that there is a another student in the system with NUSNET IDE1234569without consultation. - Execute the command:
add_consult i/E1234569 from/20251010 1430 to/20251010 1530 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with a consultation from
Add a consultation (Incorrect date/time format)
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
add_consult i/E1234567 from/2025-10-10 14:00 to/2025-10-10 15:00 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Add a consultation (Invalid date)
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
add_consult i/E1234567 from/20251310 1400 to/20251310 1500 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Delete Consultation
Delete a consultation for a student
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567, and that the student has a consultation scheduled. - Execute the command:
delete_consult i/E1234567 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
- The consultation list is updated to remove the deleted consultation.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Delete a consultation (Student not found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
E0000000in the system. - Execute the command:
delete_consult i/E0000000 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
Delete a consultation (No consultation found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234568, and that the student does not have any consultation scheduled. - Execute the command:
delete_consult i/E1234568 - Expected:
Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Create Group
Create a new group
- Ensure that group
T01does not exist. - Execute the command:
create_group g/T01 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
- Ensure that group
Create group (Group already exists)
- Setup: Ensure that group
T01already exists in the system. - Execute the command:
create_group g/T01 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that group
Add Student to Group
Add a student to an existing group
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
E1234567. - Execute the command:
add_to_group i/E1234567 g/T01 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
- Student is updated with the new group.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student in the system with NUSNET ID
Add student to group (Student not found)
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
E0000000in the system, and that groupT01exists. - Execute the command:
add_to_group i/E0000000 g/T01 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is no student with the NUSNET ID
Add student to group (Group already contains the student)
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student with the NUSNET ID
E1234567that is in groupT01. - Execute the command:
add_to_group i/E1234567 g/T01 - Expected:
- Error message is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that there is a student with the NUSNET ID
Find Students by Group
- Find students by group
- Setup: Ensure that group
T01exists and has students assigned to it. - Execute the command:
find_group g/T01 - Expected:
- Success message is displayed.
- List of students in group
T01is displayed.
- Setup: Ensure that group
Appendix: Planned Enhancement
This section outlines potential future enhancements for the application that could improve its functionality, usability, or performance. These enhancements are not part of the current scope but may be considered for future development. Team size: 5
- Remove deprecated
create_groupcommand: Since group creation is now integrated into theadd_studentandadd_to_groupcommand, the standalonecreate_groupcommand can be removed to streamline the command set and reduce redundancy. - Enhance
mark_attendanceandmark_all_attendancecommand with attendance statusunmark: Introduce anunmarkstatus option to allow TAs to easily revert a student's attendance for a specific week if they accidentally marked them as present, absent, or excused. For example, if they accidentally marked a student as present in week 5, they can now usemark_attendance i/E1234567 w/5 status/unmarkto clear the attendance for week 5 and the icon will turn grey. - Improve 'find' command with advanced filters: Enable users to search for students using partial name. For example, searching for "Alex" would return both "Alex Yeoh" and "Alexander Tan".
- Error message enhancements: Show the specific field that caused the error in error messages to help users quickly identify and correct the missing/duplicated field. For example, if a duplicate email is entered, the error message could specify "Duplicate email format in field: email".
- Enhance
add_consultcommands by allowing one student to book multiple consultation slot: Allow students to book multiple consultation slots instead of being limited to one. This would accommodate students with varying schedules and needs. - Enhance
add_consultcommands by allowing multiple student to book the same consultation slot: Allow multiple students to book the same consultation slot, enabling group consultations. - Enhance
delete_hw i/all a/<hw id>commands by adding confirmation prompt: Before deleting a homework assignment for all students, prompt the user for confirmation to prevent accidental deletions. For example, after entering the delete command, the system could ask "Are you sure you want to delete homework for all student (yes/no)". - Reduce command word length: Shorten command words to make them quicker to type. For example, change
add_studenttoas,mark_attendancetoma,mark_all_attendancetomaaanddelete_hwtodh. - Enhance
add_to_groupcommand by allowing adding one student into multiple groups: For example, a TA can teach both CS2030S and CS2040S, and the same student can be added to both groups.